# CICD Overview
# Problems
WARNING
- Business Agility 달성을 위해 Application의 빠르고 지속적인 배포에 대한 요구 증가
- 개발과 운영 조직이 분리
- 배포로 인해 장애 발생 시 운영 조직의 책임 편중
- 배포 주기 길어짐, 배포 한번을 위해 배포 계획 수립 및 검증 작업으로 최소 몇 일 소요됨
- Application의 복잡도 증가
- 관리 대상 서비스/인스턴스 증가
# Solution
TIP
- 운영환경과 동일한 Infrastructure/환경에서 테스트 수행
- 반복적인 테스트 수행 및 자동화
- Code 기반으로 Development/Staging/Production 환경에 적용
- 빠른 배포 환경
- 표준화를 통한 빌드/배포 프로세스 자동화
# Process
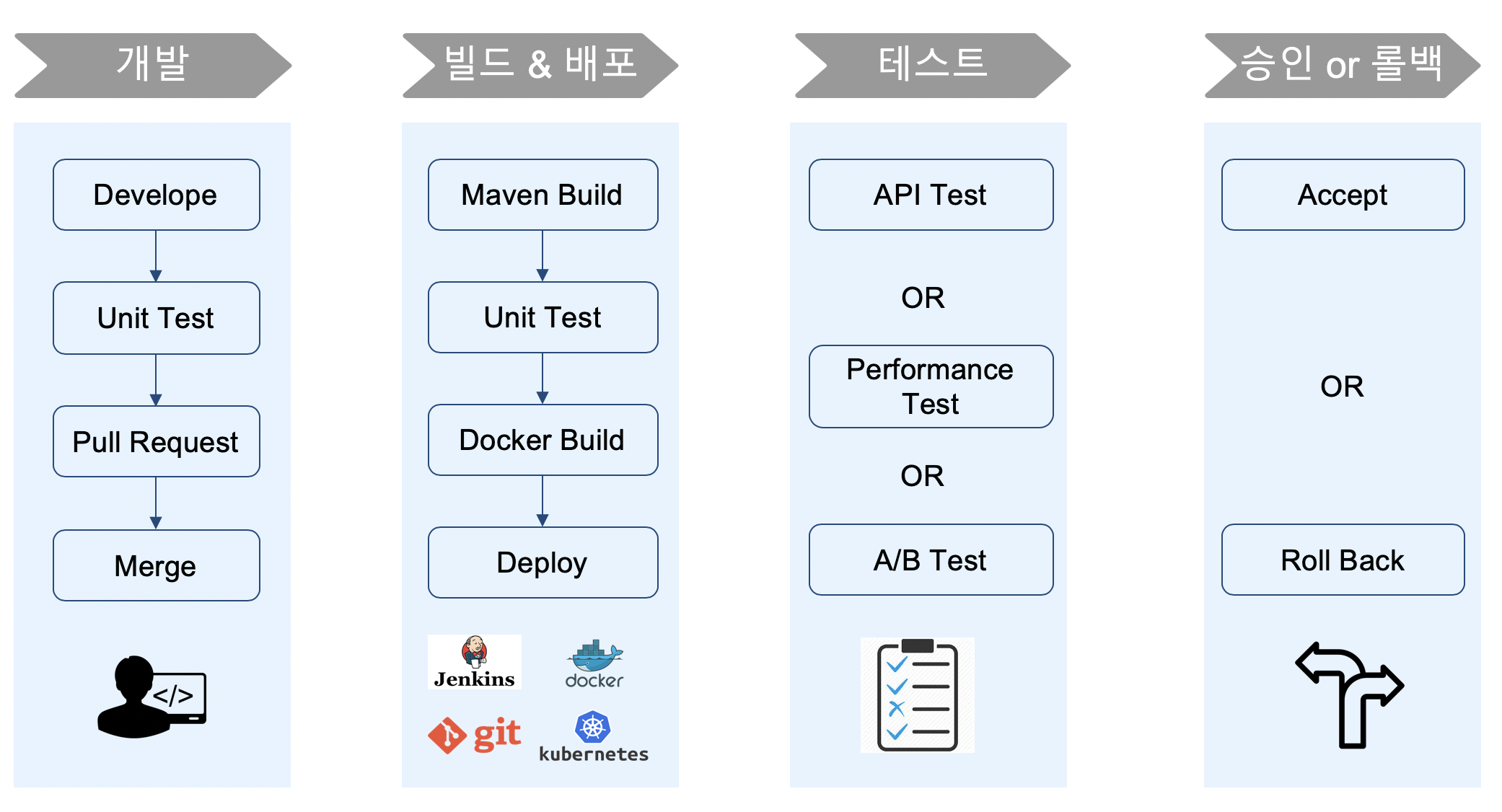
# Deploy Strategies
# Deploy in Kubernetes
TIP
- Configuration : Ingress <-> Service <-> Deployment 상호 연관 관계
- [Key]:[Value] 형태로 자유롭게 선언하여, 자원 선택시 Filter로 사용됨
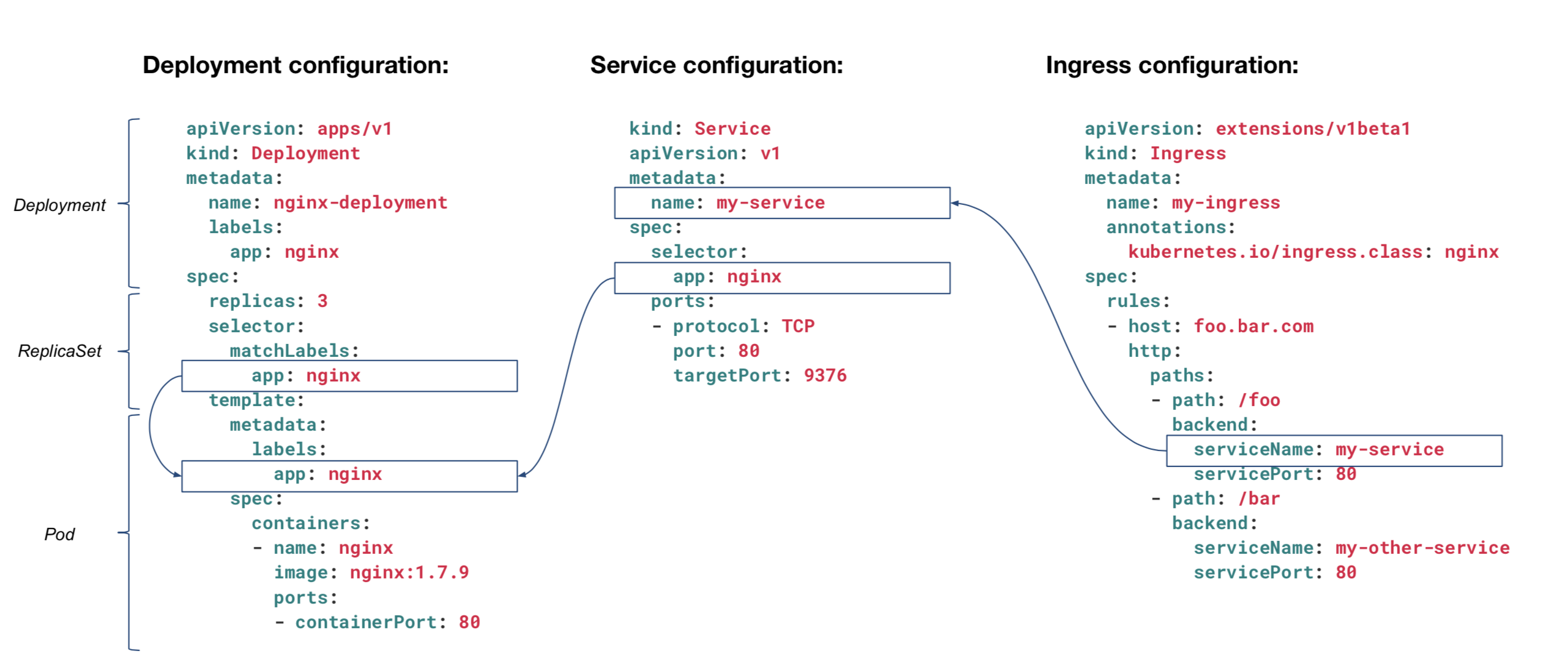 (ref. CFCF)
(ref. CFCF)
# Recreate
Application을 중단하고, 새로운 Application을 배포함.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy to setup | High impact on the user's request. downtime exists |
Example of yaml(manifest.yaml)
[ . . . ]
kind: Deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
strategy:
type: Recreate
[ . . . ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
Example of command
kubectl apply -f ./manifest.yaml
1
# Ramped
(aka) : incremental, rolling update 신규버전의 Application Instance 점진적으로 배포하고, 기존 배포된 버전의 Instance 수를 줄여 가는 배포 방식 Kubernetes의 History관리를 통해 Rollback 쉽게 처리 할 수 있음
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy to setup | Take time for rollout/rollback |
| No downtime | No control over traffic |
| Keep handling ongoing rebalancing of data |
Example of yaml(manifest.yaml)
[ . . . ]
kind: Deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollngUpdate:
maxSurge: 2 # how many instances(pod) to add at a time
maxUnavailable: 0 # unavailable number of instances(pod)
# can be unavailable during the rolling update
[ . . . ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Example of command
kubectl apply -f ./manifest.yaml
1
Traffice
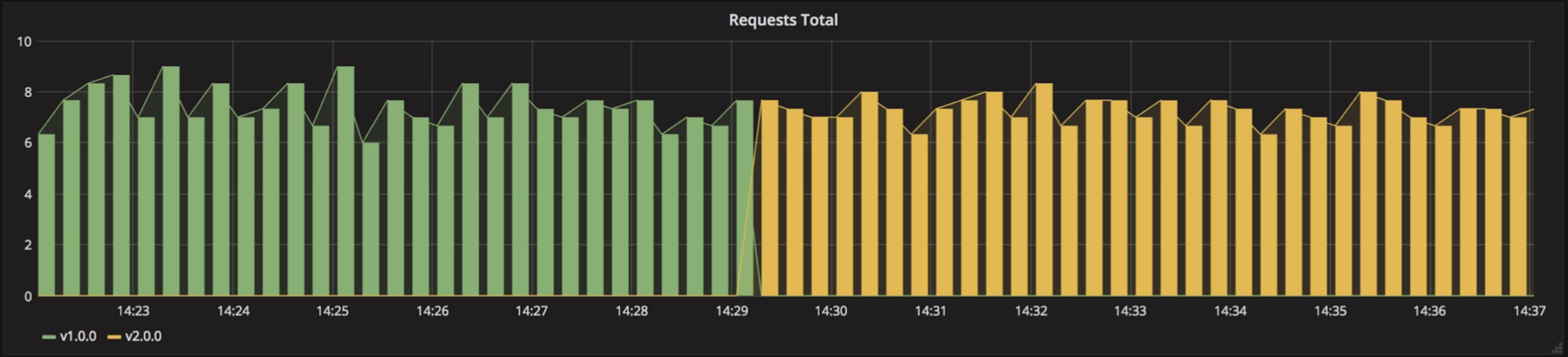
# Blue/Green
(aka) : red/black 신규버전의 Application Instance 배포하고, 기존 Instance에 연결되는 Routing 정보를 신규 Instance로 변경. 서비스 변경이 완려되면 기존 Instane는 삭제처리함.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Instant update | Expensive, need double the resources |
| Good for frontend | Should proper test of the entire platform before releasing |
Example of yaml(manifest-v2.yaml)
[ . . . ]
kind: Service
spec:
# Match both the app and the version
# When switch traffic, update the label version with v2.0.0 for version 1.0.0
selector:
app: my-app
version: v1.0.0
[ . . . ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Example of command
kubectl apply -f ./manifest-v2.yaml
kubectl patch service my-app -p \
'{"spec": {"selector": {"version": "v2.0.0"}}}'
kubectl delete -f manifest-v1.yaml
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
Traffic
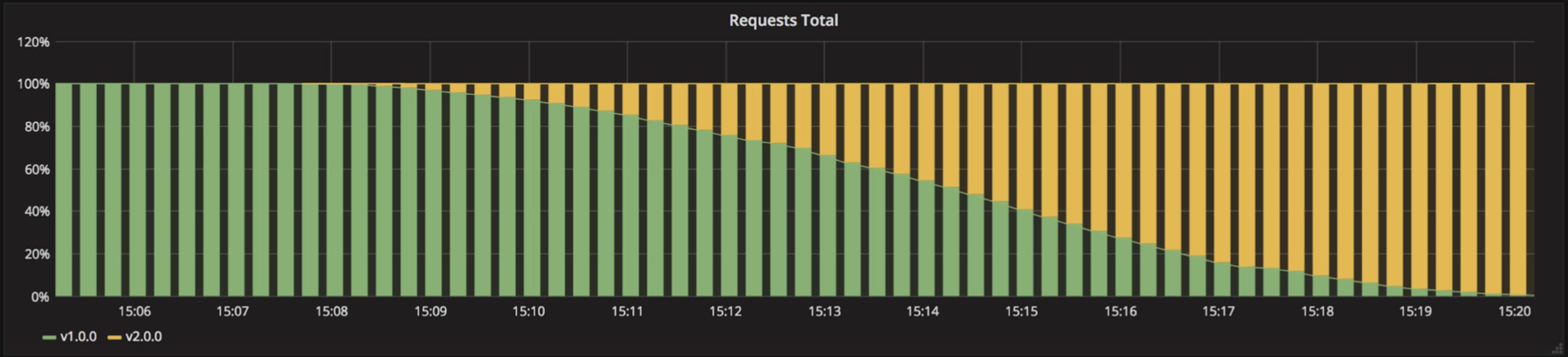
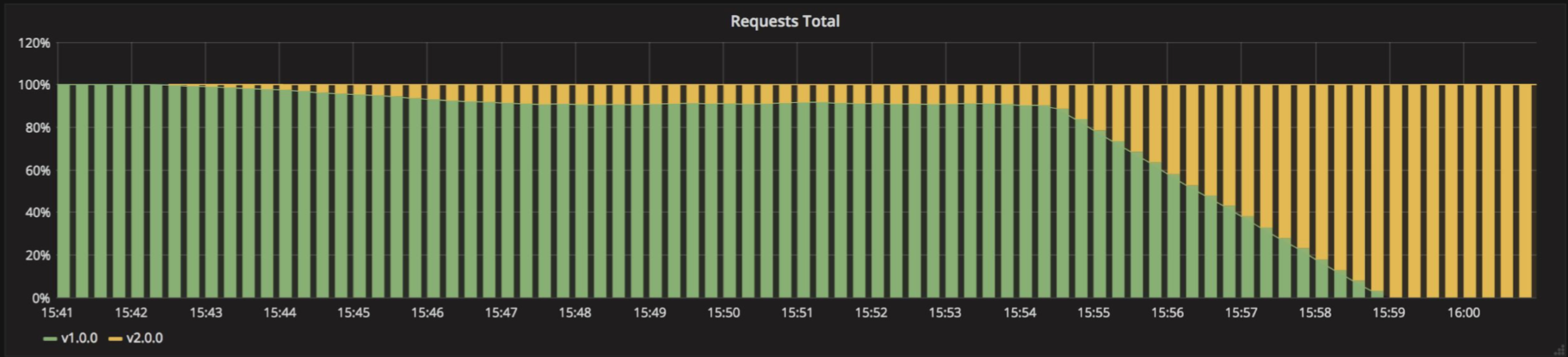
# Canary
Ramped 배포 방식과 유사하나, Instance 일부를 선배포하고, 검증 이후에 잔여 instance 모두를 배포하는 방식 선배포 검증에 실패할 경우 기존 Instance로 Rollback 처리함.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Verison released for a subset of users | Slow |
| Convenient for error rate and performance | Sticky sesisons might be required |
| Fast rollback | need traffic control required like istio or linkerd |
| 1 | 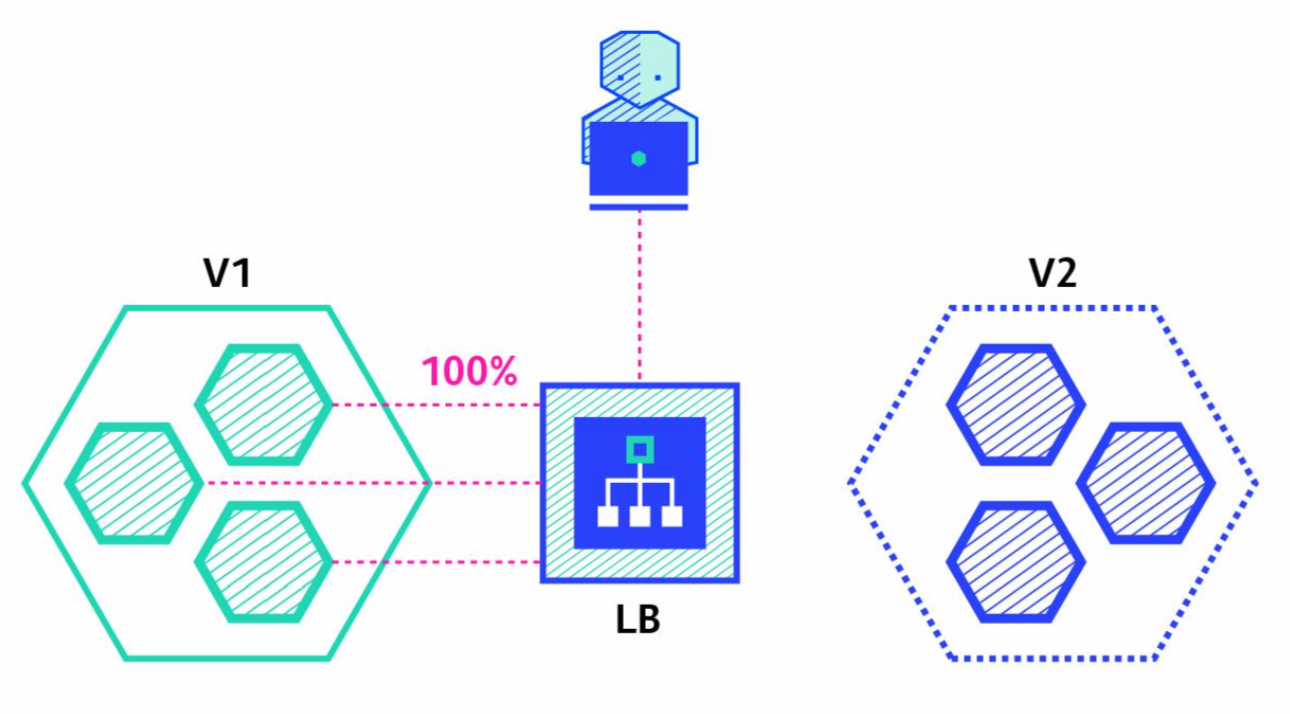 |
|---|---|
| 2 | 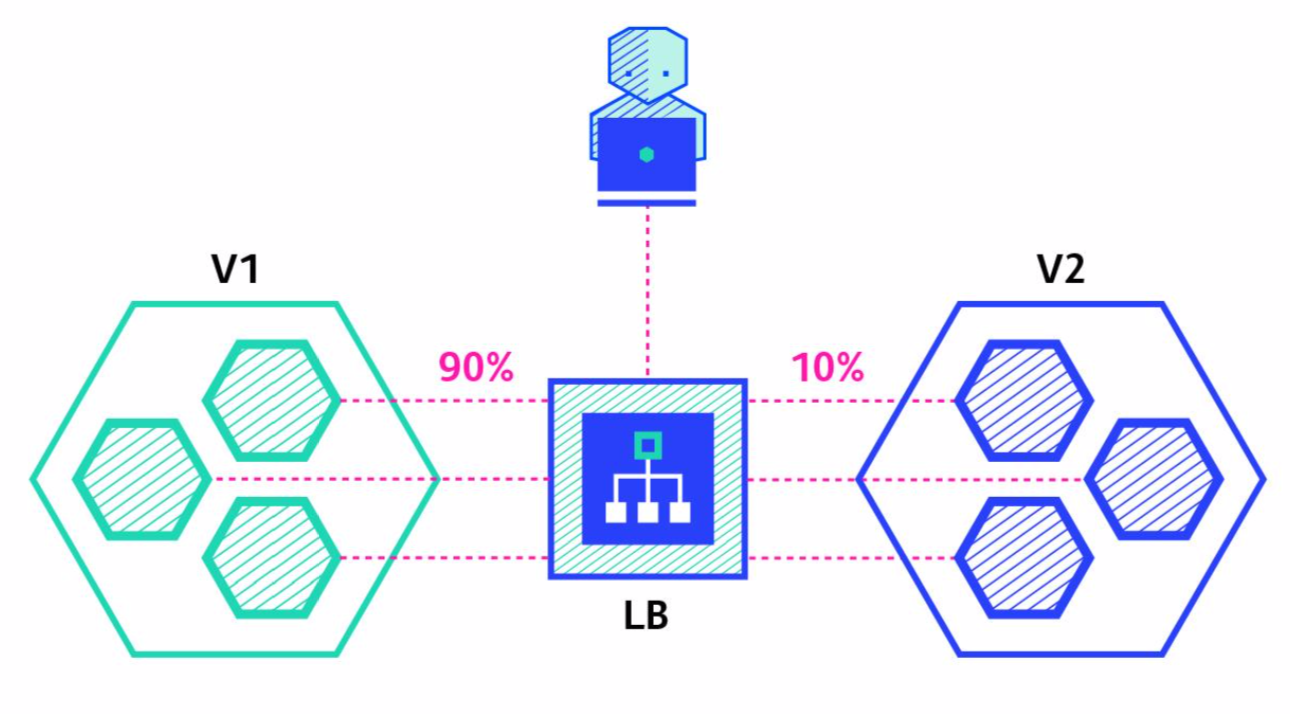 |
| 3 | 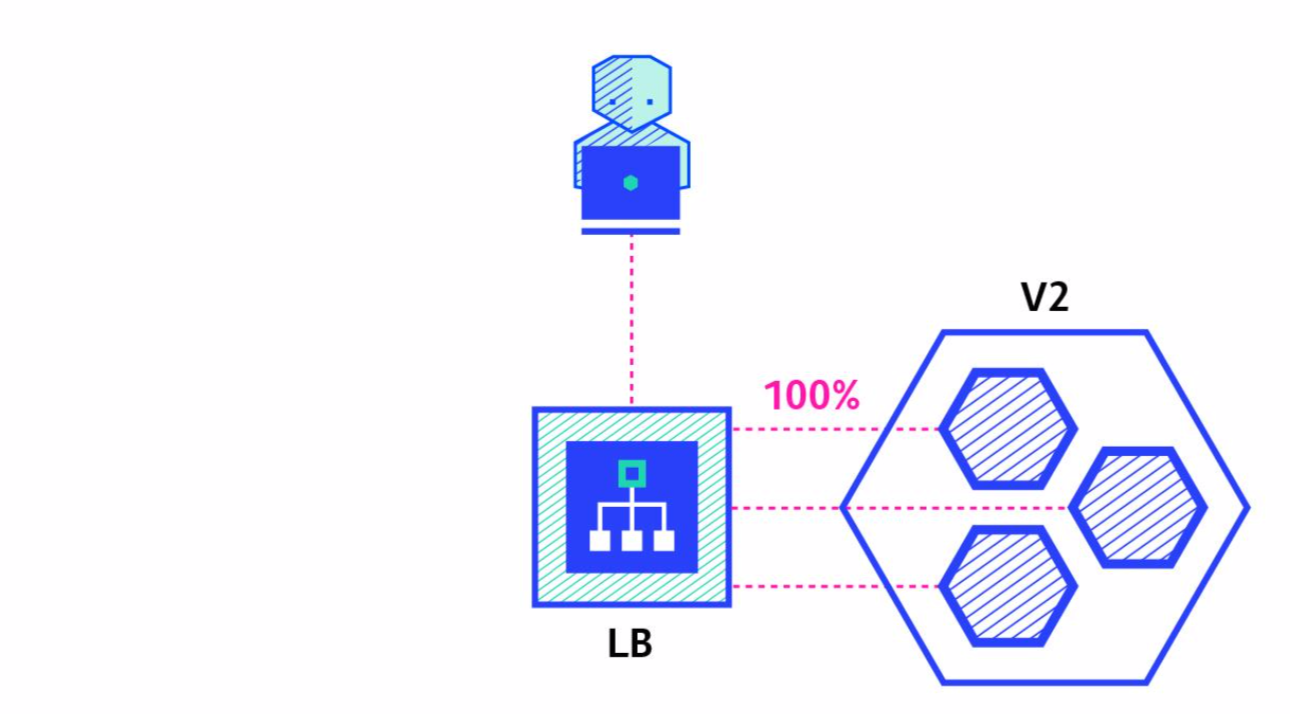 |
Traffic
# Others
- A/B Testing
- Canary 배포와 유사하며, 필요에 따라 유입되는 요청을 각각의 버전에 배분. 사용성 테스트를 수행함
- 유입되는 요청은 네트웍 비율 기반, http header의 조건 값 등 다양한 조건을 처리가 가능해야함
- Application에서 조건과 테스트 결과 값을 처리해야함
- Shadow
- 유입되는 요청에 대해, 테스트 환경으로 함께 전달되어 테스트 할 수 있는 환경
- Shadow Instance에서 처리된 결과 값은 실제 Client에게 전달되지 않음
# Summary
- recreate if downtime is not a problem
- recreate and ramped doesn’t require any extra step (kubectl apply is enough)
- ramped and blue/green deployment are usually a good fit and easy to use
- blue/green is a good fit for front-end that load versioned assets from the same server
- blue/green and shadow can be expensive
- canary and a/b testing should be used if little confidence on the quality of the release
- canary, a/b testing and shadow might require additional cluster component